smoothing
Applies a mesh smoothing operation on a solid.
Signatures
- smoothing()
- smoothing( float strength, int iter )
- smoothing( float strength, int iter, bool quality )
Details
The application of the smoothing modifier results in the execution of one or more steps of a mesh smoothing algorithm on the solid. The number of iterations can be set with the iter parameter.
The intensity of a single smoothing steps can be controlled with the strength parameter. This allows to switch smoothly between the usage of a Taubin smoothing algorithm [Taubin95] and a Laplacian smoothing. A Laplacian smoothing has a significantly higher smoothing intensity. On the other hand it suffers from shrinking, when used extensively.
The quality flag can be used to toggle between two priority modes: if set to true, the mesh surface quality is improved whereas the process speed is higher if quality is set to false.
Example
solid bunny = mesh( "bunny.stl" )
for( int s = 0; s < 4; ++s )
for( int i = 0; i < 3; ++i )
make translation( 0.16 * <[s,i]> ) >> smoothing( ((float) s)/3, pow(10,i) ) >> bunny
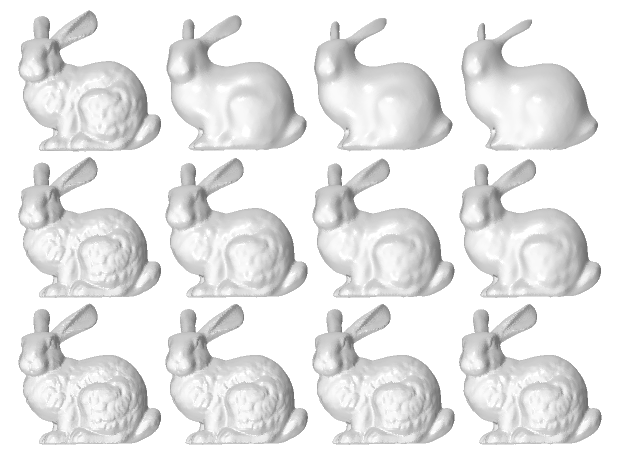

Transition between a pure Taubin smoothing (left column) and a pure Laplacian smoothing (right column) when applied for 1 (bottom row), 10 (middle row) and 100 (top row) iterations.
Casts To
Literature
- [Taubin95]
-
G. Taubin: A Signal Processing Approach To Fair Surface Design, Proceedings of ACM SIGGRAPH 95, 1995, pages 351–358
Parameters
- strength
-
Controlls the strength of the smoothing. A value is expected to be inbetween 0 (pure Taubin smoothing [Taubin95], weak effect) and 1 (pure Laplacian smoothing, strong effect). Default value is 0.
- iter
-
Number of iterations the smoothing steps are applied. Default is 1.
- quality
-
If set to true, the mesh surface quality is enhanced for the cost of a slower processing. If set to false, the process is faster but has a tendency for developing uneven regions. Note that the strengths and shape of this effect is highly dependent on the initial mesh quality and on the other parameters.